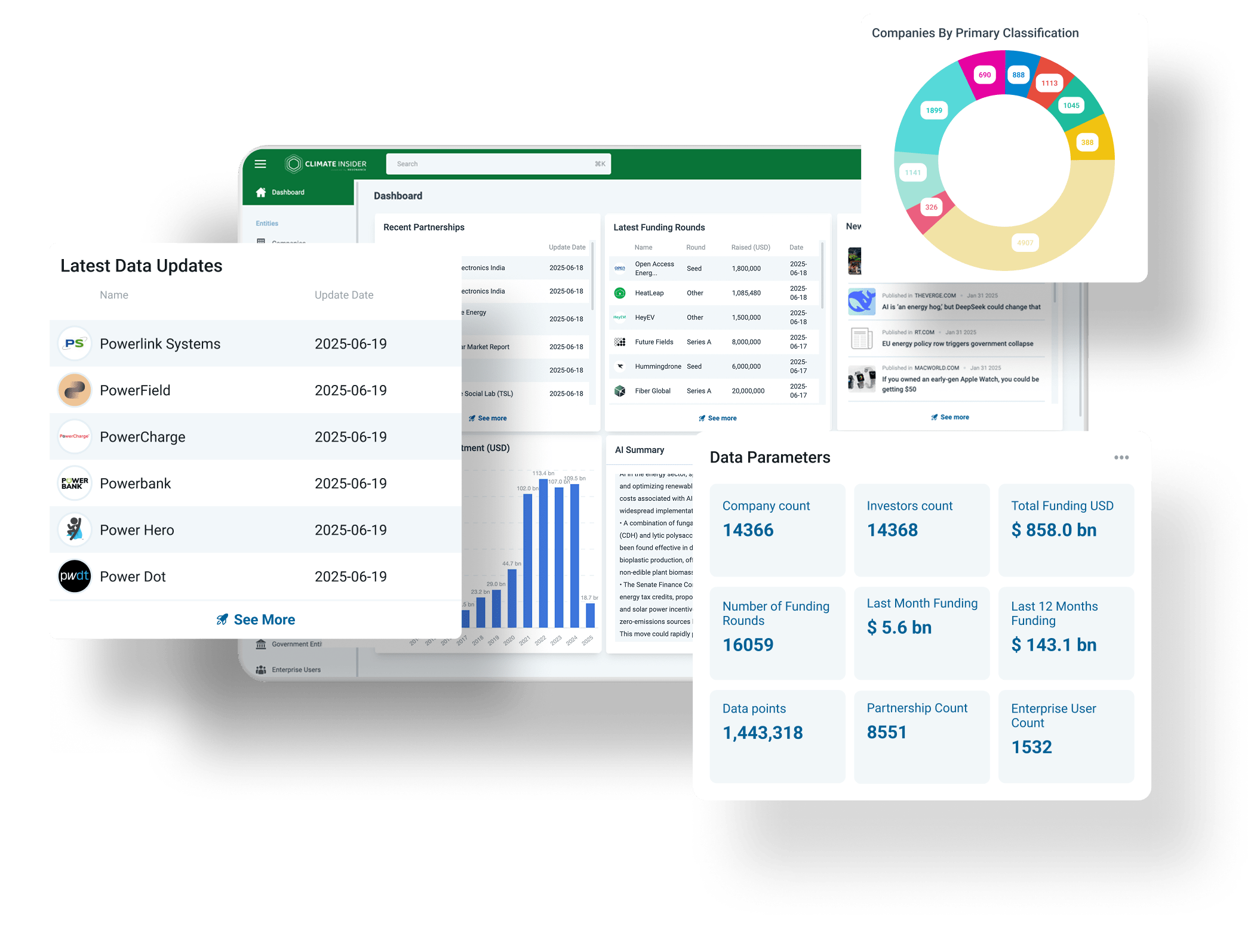
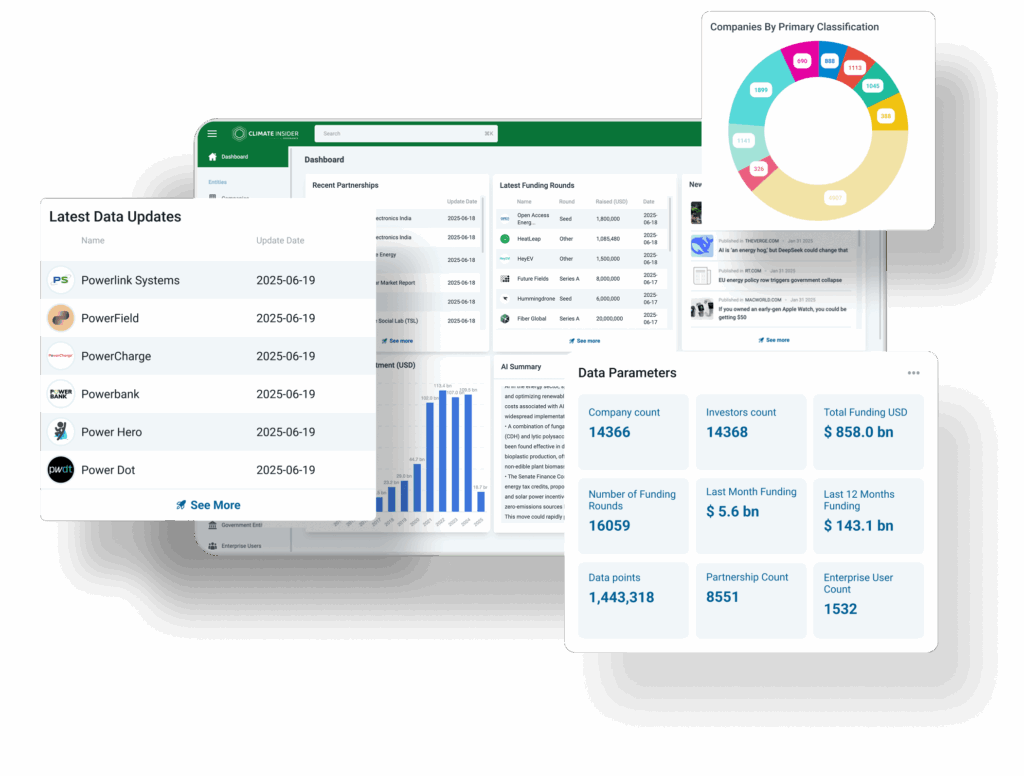
Climate Insider Brief:
- The study highlights three innovative approaches, termed “blue carbon,” aimed at preserving and enhancing the carbon-capturing potential of ocean and coastal ecosystems.
- The study emphasizes the need for a comprehensive understanding of their socio-political implications, including cultural, political, and economic factors.
- Contextual factors such as location, cultural values, and timing also influence their effectiveness. Collaborative efforts and mindful implementation are crucial for ensuring a sustainable future for our planet amidst climate change.
A study recently published in Environmental Science & Policy unveils three innovative climate solutions aimed at preserving and enhancing the carbon-capturing potential of ocean and coastal ecosystems. Led by climate scholars from Boston University, Aarhus University, and the University of Sussex Business School, this research sheds light on previously understudied interventions in marine habitat protection, offering hope in the fight against climate change.
Termed “blue carbon,” these interventions seek to safeguard or increase the natural carbon storage capacity of marine and coastal ecosystems. With over half of the world’s biological carbon currently being captured and stored by marine organisms, the urgency to protect these habitats from threats like acidification, temperature change, storms, and pollution has never been greater. The study suggests that improved management of these ecosystems could potentially contribute up to 10% of the global emissions reductions needed to meet the targets set in the Paris Agreement.
Understanding Blue Carbon Solutions

Despite their promising potential, questions remain about the efficacy and wider impacts of these blue carbon solutions on socio-political systems. Lead author Benjamin Sovacool emphasizes the need for a comprehensive understanding of these interventions’ ties to cultural, political, and economic systems as they become more widely deployed.
Drawing on extensive research including expert interviews, site visits, and document analysis, the study evaluates three key blue carbon innovations:
1. Coral Reef Preservation in Australia: Coral reefs play a crucial role in blue carbon capture, with coral tissues absorbing carbon dioxide and bicarbonate. The study identifies a narrative of crisis and urgency surrounding the preservation of the Great Barrier Reef, motivating exploration into experimental technologies such as genetic editing and cloud brightening. Positive impacts of reef preservation include boosting eco-tourism and fisheries, while potential negative impacts include the risk of invasive species outbreaks.
2. Seagrass Restoration in the United Kingdom: Seagrass meadows directly capture carbon through biomass growth and organic particle trapping. Restoration efforts emphasize the unique and valuable role of seagrass ecosystems in carbon storage. However, the innovation in seagrass restoration requires significant advancements in marine science and data collection, making it a relatively costly and slower process. Potential benefits include water quality improvement, biodiversity promotion, and erosion prevention.
3. Seaweed Cultivation in the United States: Seaweed cultivation aims to increase carbon capture by growing massive kelp beds in the deep ocean. The narrative surrounding this innovation revolves around technological advancement and profit generation while fulfilling a duty to save the oceans. However, challenges such as social acceptance and potential uncontrolled growth hinder its widespread adoption. Benefits include increased food production, improved water quality, and waste treatment.
Anticipating the Future of Blue Carbon Innovations
The study’s findings highlight the importance of narratives, innovation styles, and co-impacts in determining the success of blue carbon technologies. Contextual factors such as location, cultural values, and timing also play a significant role. The researchers anticipate that blue carbon innovations will become increasingly relevant and popular in scientific policy and discovery, offering a glimpse into a promising future for ocean and coastal ecosystem preservation in the face of climate change.
In conclusion, these pioneering climate solutions offer hope in the battle against climate change by harnessing the carbon-capturing potential of ocean and coastal ecosystems. However, their success hinges on comprehensive understanding, collaborative efforts, and mindful implementation to ensure a sustainable future for our planet.
To stay informed about the climate industry explore our latest climate news.
SOURCE: EurekAlert
Featured Image: Credit: Boston University