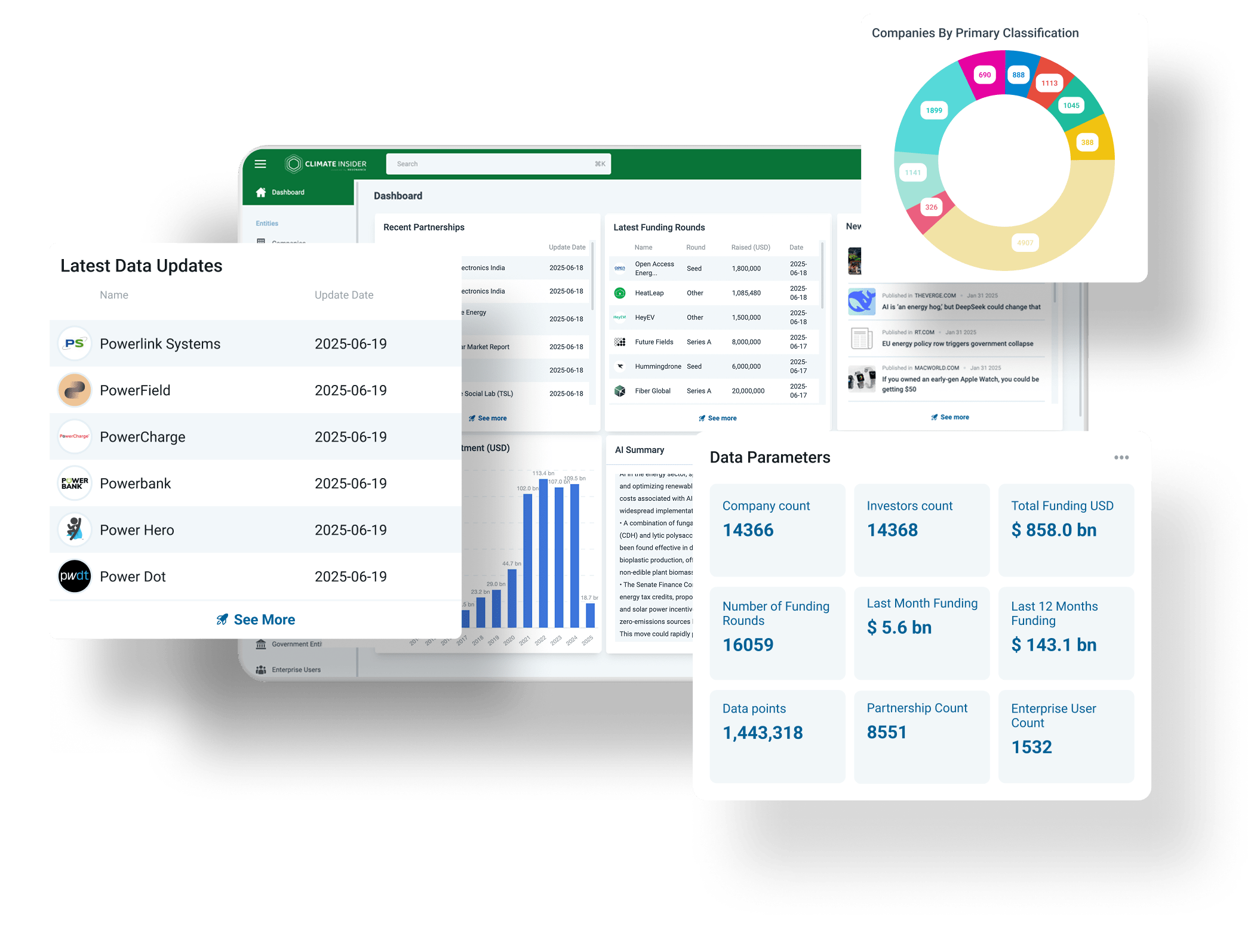
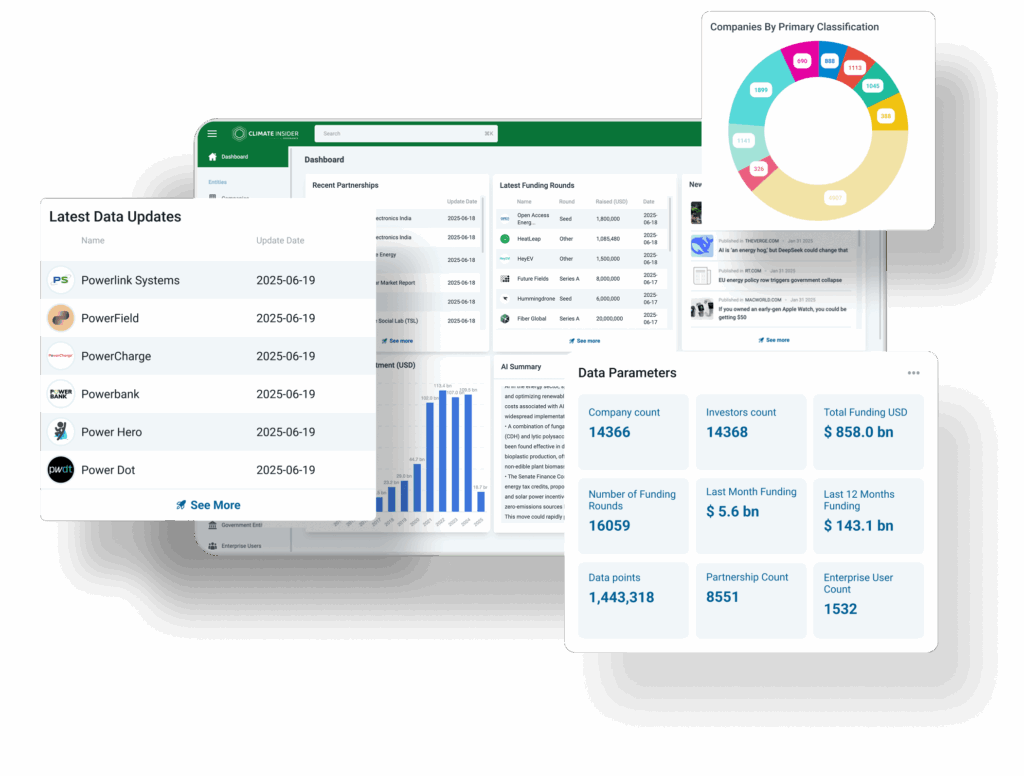
Waste is one of the last segments for us to cover under our taxonomy for climate technology. It is a fitting topic to leave until the end, as climate technologies, at their core, are arguably all about waste. Whether we are working to eliminate carbon emissions, prevent energy loss, or create a more sustainable circular economy, the concept of waste—material or energetic—is central.
Waste is a broad subject. Every sector of society—from agriculture to manufacturing to services—generates waste.
Additionally, our definition of waste is evolving beyond simply what we discard. It now encompasses underutilized resources, emissions, and inefficiencies across all sectors.
The result? Waste technologies are now permeating other markets we’ve previously explored(see below for a full list). We’ve already featured waste-to-energy technologies under Energy. Waste issues and their mitigation are also significant in Food and Agriculture, where we highlighted many companies. Carbon Management included carbon utilization, which aims to treat carbon emissions as a resource rather than a waste product.

Waste is not only an expansive issue but an expensive one.
The annual cost of dealing with waste produced globally is expected to double by 2050, reaching $640 billion, if current trends continue. As the importance of limiting waste continues to grow, innovation in climate technology is essential. From advanced recycling systems to waste-to-energy solutions, companies are developing new ways to reduce, reuse, and repurpose waste.
This shift toward a circular economy, where materials are kept in use for as long as possible, is critical for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources.
Ultimately, waste management and climate technologies are inseparable in the quest for a more sustainable future. By addressing the full lifecycle of products—from production to disposal—these technologies not only mitigate environmental damage but also open up new economic opportunities. As more startups tackle waste challenges across sectors, the potential for reducing the global waste burden and addressing climate change becomes clearer.For our taxonomy, we have organized waste management technologies under 5 key segments: waste prevention and reduction, advanced recycling technologies, waste-to-resources, industrial symbiosis and waste valorization, and specialized waste management.Given the overlap of some of these technologies, the placement of companies on the map can be somewhat subjective.
Although we haven’t explicitly categorized the circular economy under waste, the technologies and startups driving climate innovation are deeply rooted in its principles. These efforts focus on designing systems that minimize waste, promote reuse, and create closed-loop processes, all aimed at fostering a more sustainable future.
Rather than an exhaustive list, this market map presents a cross-section of scaling ventures that illustrate the breadth and depth of climate tech innovation in the waste management space.
1. Waste Prevention and Reduction
Waste prevention focuses on minimizing the amount of waste generated, while reduction targets look to decrease the volume and toxicity of waste at the source. This category includes strategies such as redesigning products for longevity, promoting reusability, and optimizing manufacturing processes to reduce byproducts and inefficiencies.
Emerging Technologies:
- AI and IoT for Smart Waste Monitoring: Startups are using AI-driven analytics and IoT sensors to track waste production in real time, enabling businesses to understand and reduce inefficiencies.
- Sustainable Packaging: Some startups are creating alternative packaging materials that are biodegradable or recyclable, such as seaweed-based packaging or bio-polymers.
- Eco-design Platforms: Startups are also developing digital platforms that enable companies to design products with lower environmental impact from the outset.
2. Advanced Recycling Technologies
Advanced recycling encompasses innovative processes that go beyond traditional mechanical recycling to convert waste materials into reusable forms. These processes aim to increase the recovery rate and quality of materials such as plastics, metals, and electronics.
Emerging Technologies:
- Chemical Recycling: This technology involves breaking down plastic waste into its original chemical components, allowing it to be reused in producing new plastic..
- Robotic Sorting: AI-powered robotic systems are being developed by startups to improve the efficiency and accuracy of sorting materials in recycling facilities, making the process faster and reducing contamination.
- Pyrolysis and Gasification: These advanced thermal treatments are used to convert organic materials (e.g., plastics) into syngas, fuels, or other reusable materials. Startups are applying this technology to improve recycling processes for difficult-to-recycle plastics for example.
3. Waste-to-Resources
Waste-to-resources involves the transformation of waste materials into valuable products, such as energy, fertilizers, and raw materials for manufacturing. This field is particularly relevant to the circular economy, where waste is seen as a resource.
Emerging Technologies:
- Waste-to-Energy (WTE): Waste-to-Energy Startups are developing systems to convert municipal and industrial waste into electricity, heat, or fuel through processes such as incineration, anaerobic digestion, and gasification.
- Composting and Biogas Production: Organic waste is being transformed into nutrient-rich compost or biogas (a renewable energy source).
- Material Recovery Facilities: Innovative startups are creating advanced material recovery facilities that extract valuable raw materials from electronic waste, construction debris, and industrial byproducts.
4. Industrial Symbiosis and Waste Valorization
Industrial symbiosis refers to the collaboration between industries to use waste from one company as a resource for another. Waste valorization involves turning waste materials into more valuable products, thereby adding economic and environmental value.
Emerging Technologies:
- Byproduct Exchange Platforms: Startups are developing digital platforms that connect industries for byproduct exchanges. For example, one company’s waste heat or materials may be repurposed by another, creating closed-loop production systems.
- Carbon Capture and Reuse: Technologies that capture CO2 emissions and convert them into products like fuels, chemicals, or construction materials are becoming increasingly popular in industrial symbiosis.
- Resource Efficiency Software: Startups are also building software tools that optimize resource use in industrial processes, helping companies minimize waste and find new uses for byproducts.
5. Specialized Waste Management
Specialized waste management focuses on handling and processing specific types of waste, such as hazardous materials, e-waste, medical waste, and radioactive substances. These waste streams require tailored solutions to ensure safe disposal or reuse.
Emerging Technologies:
- E-waste Recycling Technologies: Startups are using technology to improve the recycling of electronic waste by safely extracting metals, plastics, and other components.
- Hazardous Waste Treatment: Some startups are developing new chemical processes for safely neutralizing hazardous waste, including medical waste from hospitals and industrial chemicals.
- Blockchain for Waste Tracking: Blockchain is being used by startups to track the entire lifecycle of waste, ensuring proper handling and compliance with regulations, particularly in industries that generate hazardous or regulated waste.
CI Market Maps
Be sure to check out the other Climate Insider Market Maps in our series:
- Overview
- Food and Agriculture
- Energy
- Transportation
- The Built Environment
- Industry
- Carbon Management
- Hydrogen
Recent articles from the CI website
- Climate Insider Tech of the Week – Waste Management
- Greyparrot, Based in London, Secures $12.8M for AI-powered Waste Analytics
- Samsara Eco secures $100M in Series A+ funding to help end plastic waste (climateinsider.com)
Some of the companies on the map

Anaergia
Carbon Cleanup
GeoFluxus
NaturLoop
Recycleye
Grey Parrot
Circularise
Agrobics
Phenix
Miwa
Bioelektra Group
Waga Energy
Swappie
Green Mining
Miniwiz
Waste4Change
The Plastic Bank
Aqua Metals
Resourcify
Carbios
Circular Systems
Loliware
iWaste
OLIO
Too Good to Go
Banyan Nation
Agilyx
Recresco
Lithium Battery Recycling Solutions
Mura Technology
ReNew ELP
Pyrowave
Greenmantra Technologies
Gr3N SA
Clariter
Renasci
So Max Circular Soultions
HTCycle
Meva Energy
TerraCycle
Reworld Waste
Renewi
Indaver
Plagazi
Vanguard Renewables
UBQ Materials
HomeBiogas
Recology
Rubicon
Aspire
Recircular
Vattenfall
WA3RM
Cylib
Enevo
Kitro
Neolitik
Zaak Technologies
Genecis Bioindustries
Pyrowave
Wasterobotics
CleanRobotics
Bin-e
WasteControl
WasteHero
Nordsense
Airex Energy
Ronin8
SonoAsh
Recycling Technologies
Plastic Energy
Lasso Loop Recycling
Pretred
Vartega
Nth Cycle
Rubicon
Apeel
Imperfect Foods
Zero
Matsmart
RoadRunner
Agricycle
GIDARA ENERGY
w2g Energy
GrinBean Smart Recycling
Myco4food
AquaLogIQ
PlasticsLoop
Pyrotask Energy
ACE Green Recycling
Attero
Basestation
Humara
Recircled
Ourobio
Mi Terro
Corumat
EnvoProtect
Metastable Materials
The Upcycl
a:gain
ReSolved Technologies
Batch.Works
DyeCoo
Alchemie Technology
Circ
Ambercycle
Mol-e
Aeropowder
Chapul Farms
Pyrocore
Waister
Altent Renewables
Arkeale