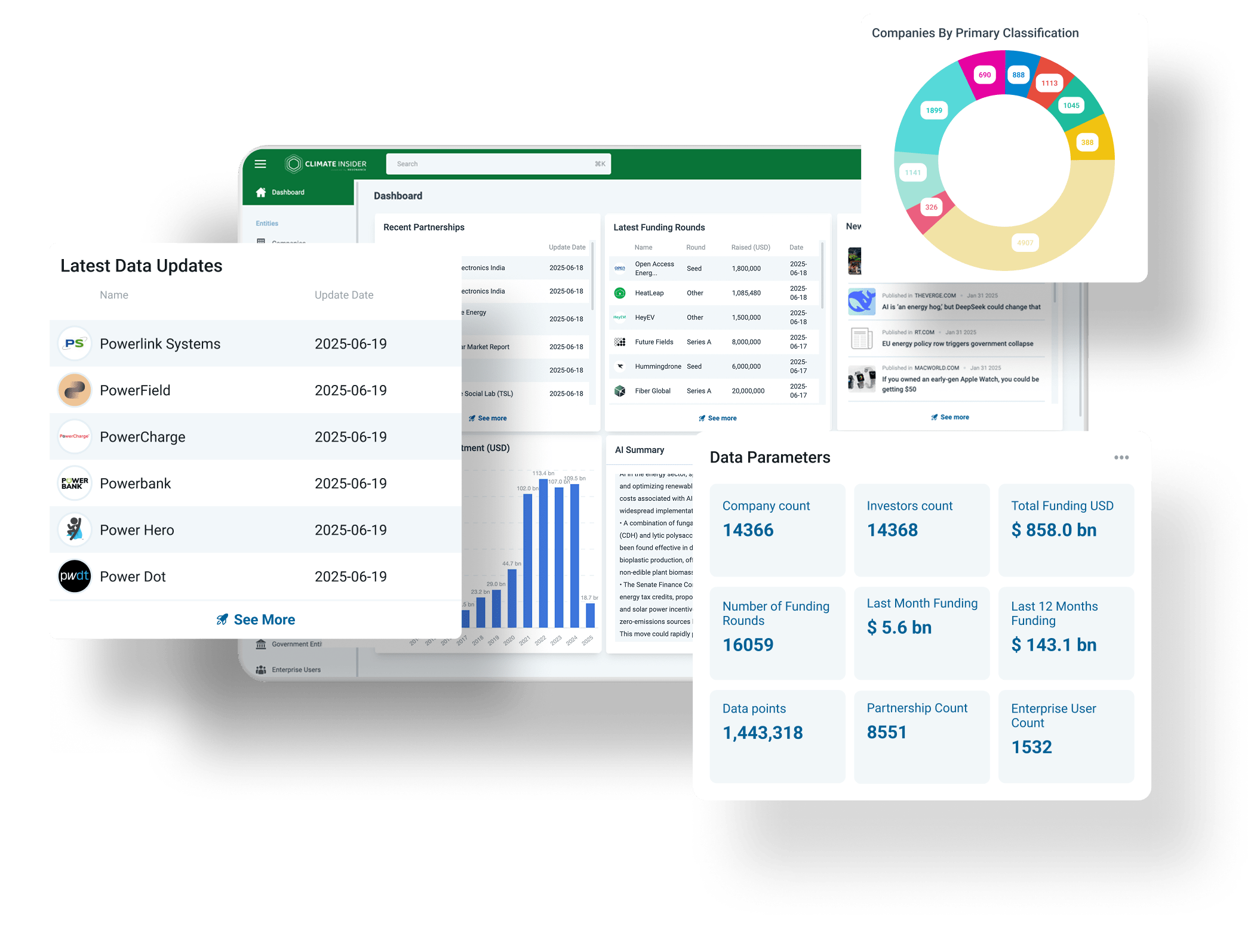
Author: Dwayne Pattison
For this segment, we not only cover transportation (movement of people), but also transport and logistics (the movement of goods) and the infrastructure related to each of these (fueling and charging stations, ports, roads, rail lines, etc).
Climate tech innovation in transportation focuses on developing technologies and solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impact of climate change. This sector is crucial as transportation contributes significantly to global carbon emissions. The subsegments we monitor and analyze are:
- Fuels
- Road
- Aviation
- Marine
- Rail
- Infrastructure and Logistics
The developments of the required infrastructure and logistics related to each of these subsegments is discussed within the respective sub sectors throughout this report.


Overview
The transportation industry is considering three primary pathways to lower emissions:
- Alternative Fuels
- Electric
- Hydrogen
The most relevant pathway is largely dependent on the type of vehicle (with considerations of onboard storage, safety and cost-effectiveness).
For light duty vehicles and personal vehicles, the obvious first choice has been electric, with some considerations for biofuels such as ethanol. Hydrogen is emerging as another potential option. For larger, heavy duty vehicles and equipment, such as semi trailers, the switch to electric is less straightforward, and therefore, hydrogen-powered engines and diesel alternatives (such as biodiesel) are potential solutions.
For the transport sectors too, electric is not the immediate first choice. In rail and aviation, hydrogen and biofuels are being strongly considered and developed. For the marine industry, biofuels, ammonia and methanol are all being evaluated for replacing diesel.
Travel distance is also a factor in the path selection. Electric is often the best option for shorter distances for city buses, marine, air, rail (light rail within cities for example) and micro-mobility (e-bikes, scooters, etc.). For longer haul trips, hydrogen (including ammonia and methanol) and biofuels are thought to be better options currently.
Fuels
We consider fuels first as they play a central role in the decarbonization of the transportation industry. All industries discussed below including vehicles, aviation, shipping and rail are employing these fuels at varying degrees.
The fuels we cover include biofuels, hydrogen, hydrogen carriers (ammonia and methanol), and e-fuels.
Biofuels
Biofuels like biodiesel and ethanol are being developed as alternatives to fossil fuels. Ethanol is usually made from the fermentation of crops such as corn, sugarcane and wheat. Biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils (e.g. canola oil), animal fat and recycled cooking oils.
Another set of fuels are called advanced biofuels, which are evaluating alternative biomass sources such as algae, agricultural residue and other types of waste. Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs) are a category of non-conventional aviation fuels that are designed to be more environmentally friendly than traditional jet fuels. They are also derived from various sources of biomass.
Biofuels are considered climate neutral as approximately the same amount of CO2 is released during combustion as is stored by the crops as they grow. GIven that they can replace fossil fuels directly, they can lower emissions in the transportation sector while allowing for the continued use of conventional vehicles.
Startups are actively involved in this segment on many different fronts. Companies are identifying more feedstocks that can be used in production – focusing on waste materials. Some companies are improving the production processes themselves, working to make them more efficient. Additionally, startups are exploring opportunities to integrate renewable energy and CCUS in the manufacturing process.
Given that biofuels are derived from biomass, we also discuss them in our Market Maps for Energy (link) and Food and Agriculture (link). Check them out at the links.
E-fuels
Electronic fuels or e-fuels are a subset of synthetic fuels which are manufactured using renewable energy. The goal being to produce a drop-in replacements for traditional hydrocarbon fuels. In this way the fuels used in existing internal combustion engines.
E-fuels are synthesized using carbon dioxide (captured from the atmosphere or industrial sources) and hydrogen, where the hydrogen is produced using renewable electricity. Startups in carbon capture and storage and hydrogen production are therefore key players in developing e-fuels for all types of transportation.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is increasingly recognized as a pivotal element in the transition to cleaner transportation technologies. Its application in the transportation sector, particularly through hydrogen combustion engines and fuel cells, offers a promising path to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.Hydrogen is also used in the production of e-fuels (below).
- Combustion: Hydrogen combustion engines are similar to traditional internal combustion engines but are modified to burn hydrogen instead of gasoline or diesel. The primary emission from hydrogen combustion is water vapor, making it a zero-emission solution at the point of use.
- Fuel cells: Convert hydrogen into electricity through a chemical reaction, with water and heat as the only byproducts.Fuel cells are being used in a range of vehicles, from passenger cars to buses and heavy-duty trucks.
Hydrogen Carriers
Hydrogen carriers are compounds that can store and release hydrogen. They are used to transport hydrogen in a more stable or convenient form compared to hydrogen itself. Like hydrogen, they can either be combisted directly in an engine or used in a fuel cell.
- Ammonia (NH₃): Produced by combining hydrogen with nitrogen, ammonia can be used to transport and store hydrogen energy. It releases hydrogen upon decomposition.
- Methanol (CH₃OH): Methanol can be synthesized from hydrogen and carbon dioxide and can be reformed to release hydrogen.
These fuels can be zero-emission if produced from green hydrogen (i.e produced from renewable energy). They are particularly promising for shipping.
Electrification
The electrification of transportation is a pivotal aspect of the global effort to combat climate change. As the world seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and move towards a more sustainable future, the transformation of our transport systems – encompassing road vehicles, marine, air, and rail – plays a crucial role.
Road
The road transport sector, including personal vehicles, buses, and trucks, is at the forefront of the electrification movement. Electric vehicles (EVs), powered by batteries and electric motors, offer a zero-emission alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. The rapid advancement in battery technology, resulting in longer ranges and shorter charging times, along with the expansion of charging infrastructure, is accelerating the adoption of EVs worldwide. This shift is crucial, as road transport accounts for a significant portion of global CO2 emissions.
Micromobility
Micromobility, a term that encompasses small, lightweight vehicles typically operating at speeds less than 25 km/h, is increasingly intertwined with electrification and climate technology initiatives. This sector includes electric bicycles (e-bikes), electric scooters, and other compact personal electric vehicles. They are powered by rechargeable batteries, offering an eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuel-powered vehicles for short distances.
Marine
The marine industry, traditionally reliant on heavy fuel oils, is exploring electrification to reduce its environmental impact. Electric and hybrid propulsion systems are becoming more prevalent in short-range vessels like ferries, pleasure boats, and small commercial ships. For larger vessels, the challenge is greater due to their immense energy requirements, but innovations in battery technology and alternative fuels like hydrogen and ammonia (as discussed above) are opening new possibilities for cleaner maritime transport
Air
Electrifying air travel presents unique challenges due to the high energy demands and safety requirements. Current efforts are focused on small electric aircraft and hybrid-electric models, suitable for short-haul flights. Research and development in battery technology and alternative fuels like hydrogen are key to enabling longer-range electric flights in the future.
Rail
Rail transport has been a leader in electrification for decades, with many networks worldwide operating on electric power. The focus now is on expanding electrification to more tracks and developing battery-powered trains and alternative fuels such as hydrogen and e-fuels for routes where electrification is not feasible.
Another type of rail that has emerged is vacuum tube transportation (better known as a “hyperloop”). The technology combines magnetic levitation (maglev) for reducing friction, vacuum tubes for creating low-pressure environments, and renewable energy sources for powering the system. They represent a revolutionary mode of transportation that involves propelling passenger or cargo pods through a low-pressure tube at high speeds. They too can potentially lower emissions in transportation if connected to renewable energy sources.
Infrastructure & Logistics
Startups in the transportation space are actively innovating in infrastructure and logistics, not only for EVs but also for hydrogen and alternative fuels. Their activities span a range of areas, from developing new technologies and services to building the necessary infrastructure for supporting a more sustainable transportation ecosystem
EV Infrastructure
- Charging Networks: Startups are developing and expanding public and private EV charging networks. This includes fast-charging stations for highways and urban charging solutions like street lamp chargers or wireless charging.
- Smart Charging Solutions: Innovations include smart charging systems that optimize charging times based on energy grid demand, vehicle usage patterns, and renewable energy availability.
- Battery Technology and Swap Stations: Some startups focus on advanced battery technology for faster charging and longer range. Others are developing battery swap stations, allowing drivers to quickly exchange depleted batteries for charged ones.
Hydrogen
- Production: Startups are working on green hydrogen production methods, using renewable energy sources to electrolyze water, which is crucial for making hydrogen a truly sustainable fuel.Some startups are focusing on small-scale, on-site hydrogen production units to overcome distribution challenges and reduce transportation costs.
- Hydrogen Refueling Stations: Building a network of hydrogen refueling stations is key for the adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles. These startups face challenges similar to EV charging networks but must also handle the high-pressure storage and distribution of hydrogen
Logistics
- Fleet Electrification: Startups are assisting companies in transitioning their fleets to electric or hydrogen vehicles, including providing infrastructure support and fleet management software.
- Data Analytics and AI: Leveraging data analytics and AI to optimize routes, reduce energy consumption, and improve overall efficiency in transportation and logistics.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technologies: Some startups are exploring V2G solutions, where EVs can feed energy back into the grid during peak demand, helping to stabilize the energy network.
Other Segments
As we do in all our maps we try to make connections to the other market maps we have, or will have, created. Not all the segments are black and white and we highlight this in the maps we create. As discussed above CCUS is an important component in producing biofuels, as is the processing of agricultural biomass. Other crossovers include:
- Waste: Startups are working on vehicle battery recycling, the recycling of tires and using other types of non-biomass waste to produce transportation fuels
- Food and Agriculture: As discussed in our first map, companies working on lowering food waste using special containers; logistics and how to transport food more efficiently is also a focus
- Grids: Grid connection and smart grid technology is important as more EVs connect to grid.
- Built: EVs can act as central battery in a small microgrid like a house. Startups are also working to develop charging stations from existing buildings.
These are just a few examples of the companies that are working across segments.
Conclusion
The transportation sector’s shift towards sustainability is driven by innovative startups across various subsegments. These companies are not only reducing emissions but also reshaping how we think about mobility and transport in the context of climate change. The future of transportation looks to be increasingly electric, efficient, and integrated with renewable energy sources.
To stay informed about the climate industry explore our latest climate news.
Companies on the Map
1Komma5
Accell Group
Air Company
Algenol
Alstom
Amogy
Angell
Aptera Motors
Arrival
Ather Energy
Ballard Power Systems
BasiGo
Beta Technologies
Beyond Aero
Bolt
Bound4blue
Bumblebee Power
BYD
Candela
Carbon ONe
Carbon Recycling International
CargoKite
ChargeLab
ChargePoint
ChargeX
Charzer
Clean Motion
Clear Flame Engine Technologies
Corvus Energy
Dat Bike
Eco Marine Power
Einride
Electra
Enerkem
EV BOx
EVage
EVgo
Evoy
Exponent Energy
Flux Marine
FreeWire Technologies
Fulcrum Bioenergy
Gevo
Gogoro
Greencell Mobility
Greyp Bikes
GT Green Technologies
H2Fly
Heart Aerospace
Hexagon Purus
HyPoint
HySiLabs
Hyzon
InMotion
Intramotev Autonomous Rail
Ionomr
JEDLIX
Joby Aviation
Kate
LanzaJet
Lilium
Lime
Loop Energy
Luup
Mahindra Electric
Maka
MayMaan Research
Metafuels
Metroboard
Mobility House
My Energi
Myenergi
Nevomo
Nikola Motors
NIU
Norse Power
Numbat
Nuvve
Oceanbird
Olleco
One MOTO
Onomotion
Parallel Systems
POET
PowerX
Proterra
Quadrise
Redwood Materials
Rimac Automobili
Rivian
Rocsys
Route Konnect
Routific Solutions
Skydweller
Smartcharge
Solar Freeze
Stadler
SUN Mobility
Sun-Ways
Terra
Terrawatt Infrastructure
Tesla
Tevva
TFS Cargo Cycles
Tier
Tiler
Titan Hydrogen
Transpod
Trucksters
Universal Hydrogen
Upway
VADE
VanMoof
Vayve Mobility
Velocys
Voi Technology
Volta Trucks
Wastefront
WeaveGrid
yego
Yulu Bike
ZeroAvia
Zerojet
ZEV Station
Zin Boats